One of the best inventions humankind has brought into this world are temperature control systems, namely: air conditioning, heating, and ventilation systems. In warm weather, you only need to grab a remote and push a button and a cool breeze of air will come and cool your body temperature down. If the weather is too cold to the point you get chilly, with just a click of a button, you can warm your heart down to comfortable levels. If your indoor air is smelly and is otherwise unhealthy, your ventilation systems will do the trick and will give you fresh indoor air. But one system stands out among the rest in locations where cold weather is prevalent: heating systems.
Heating systems use a heat source and are fueled by either gas or electric components. In the United States, the most commonly used heating system is gas furnaces. Gas furnaces use gas as their fuel, hence the name. It may seem like it is simple to understand the way gas furnaces work. Some may think the mechanics and physics involved in gas ranges are the same with gas furnaces, but we hate to break it to you: it is not. A gas furnace is technically more complex than gas ranges since furnaces contain more components than gas ranges. But how do gas furnaces work exactly? First, let us understand what furnaces are.
What Are Furnaces?
Furnaces are heating machines involved and oftentimes integrated into your home’s HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning). These heavy and bulky machines are designed to give your home the heat and warmth you need in cold weather and distribute that heat to basically every inch and every corner of your house. Furnaces give you heat by burning fuel inside their fuel compartment to warm the air around them. Some furnaces use electricity, natural gas, or oil. But the most common furnaces used today are powered by liquefied petroleum gas, also known as LPG. Some furnaces work by boiling water inside their tanks and proceeds to distribute the heat that comes from the steam of the boiling water.
How Do Gas Furnaces Work: Heating Cycles
Understanding how gas furnaces work is no simple thing. So it is best to know about the fundamentals first before we dive deep into the more complex mechanics of gas furnaces.
In furnaces, there are heating cycles. Just like any other cycle you thought of, heating cycles are composed of stages and steps. The heating cycle of your furnace begins with an outdoor pipe leading all the way to your home. This pipe connects your furnace to the fuel source, which can be LPG or natural gas. If your furnace uses LPG, your furnace would be connected via a pipeline to the outdoor LPG storage tank. If your furnace uses natural gas, you will have underground pipelines that connect to the natural gas source. (Related: Heat Pump Or Gas Furnace: Which One Is Right For You?)
Your furnace’s heating cycle can be simplified by enumerating the stages involved:
- 1After the gas enters your home and to your furnace via the pipelines connected to your outdoor LPG tank or natural gas source, the burner in your furnace lights it, and the byproducts are flames.
- 2Then, cold air from your house enters your furnace, that is when the burning gas will make the cold air warm within the heat exchanger inside the furnace.
- 3After that, exhaust, or the byproduct of burning gas will be piped out of your furnace through a vent and will exit your home via an exhaust pipe directed outdoors.
- 4Then, the blower fan in your furnace will evenly distribute the warm air in different parts of your house and in places where the thermostat detects the need to heat up.
- 5After that, your internal room temperature will gradually rise up as the warm air is distributed evenly around the house. Cold air will eventually be redirected and go to the furnace and will be cycled again through the heat exchanger.
- 6Once your thermostat senses that the temperature you have set has been reached, it will eventually switch off the gas valve in your furnace to stop the flow of warm air.
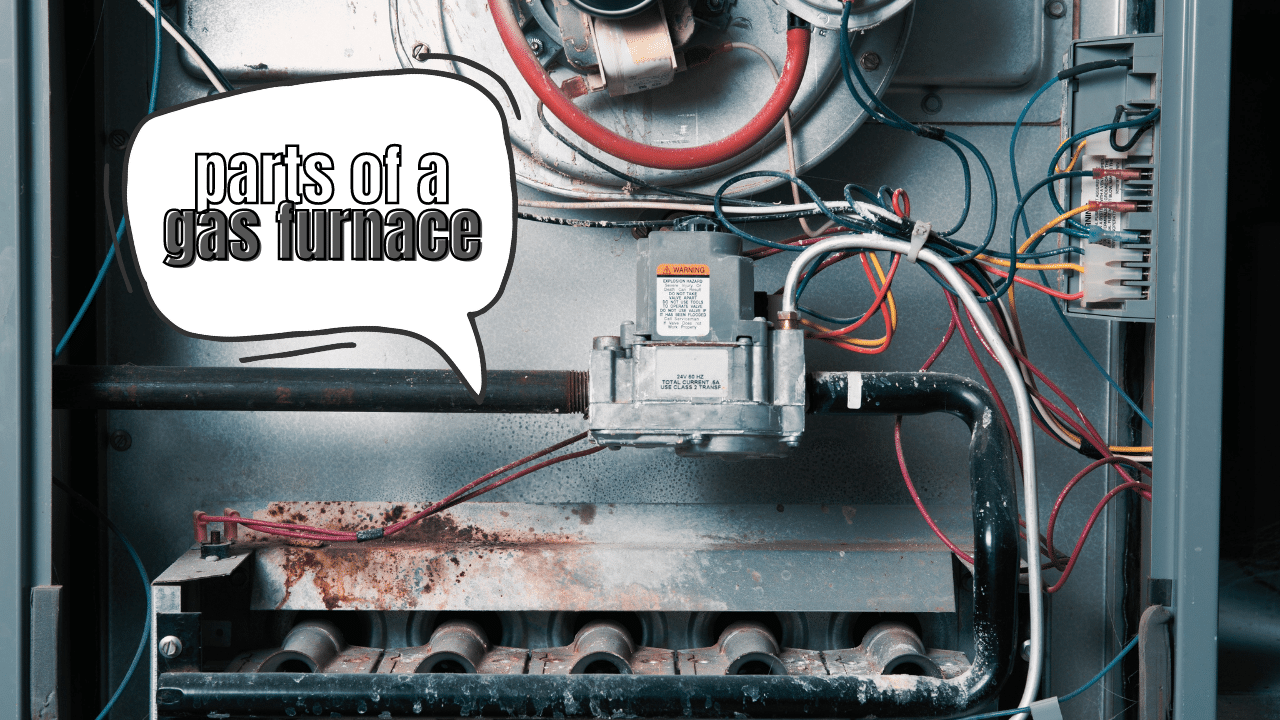
Gas Furnaces: What are the Parts?
Gas furnaces, just as we mentioned earlier, contain a lot of complex and sensitive parts inside, and these parts make the gas furnace accurate and safe. Here are the parts of a gas furnace:

Gas Furnaces: How to Maintain?
Just like any machine and appliance in your home, gas furnaces need maintenance works regularly. Air-conditioning units are maintained and cleaned to make them run smoothly without any sort of problems, and it is the same for gas furnaces, especially because these furnaces handle flammable material and can be a cause of fire or explosion if any severe malfunction occurs. Here are some tips you can do to keep your gas furnace safe and working in tip-top condition:
Conclusion
Gas furnaces are important pieces of technology that can save us from chilly weather and even hypothermia, and it is a result of beautiful engineering and innovation that can make our cold and chilly nights warm, soothing, and calming. Gas furnaces are common in the American household, and it would be nice to see furnace owners who know how the machine works so they can take care of it and make it last long. Ultimately, learning about gas furnaces is a great thing to do so you can minimize the occurrence of malfunctions through regular check-ups and maintenance works, and regular filter cleaning.